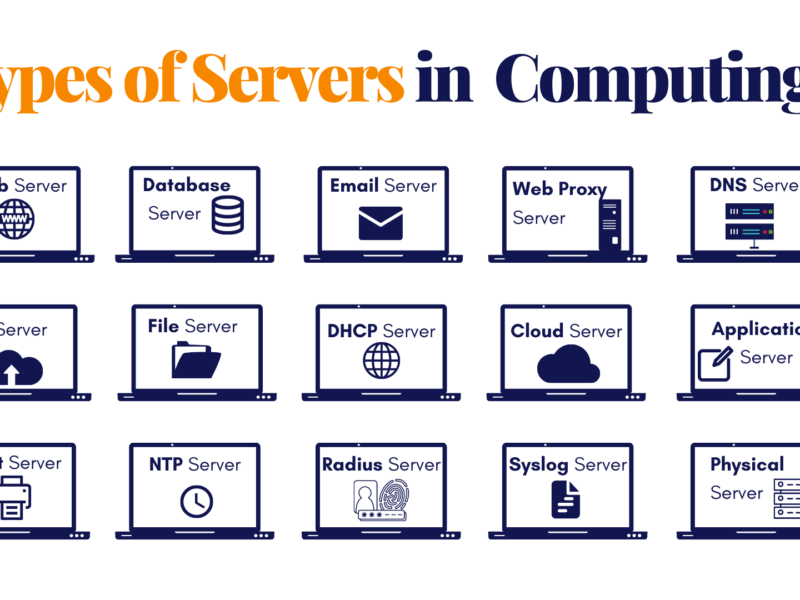
Servers include web, application, database, and file servers. Each type serves a distinct purpose. They host websites and manage data and apps.
Understanding the different types of servers is crucial for any IT infrastructure. Servers are the backbone of the Internet and modern business. They enable web hosting, data storage, application delivery, and network management. Web servers like Apache and Nginx deliver web content to users’ browsers.
Application servers, like Tomcat or WebSphere, run and manage apps. They provide an environment for this. Database servers, like MySQL and Oracle, manage vast amounts of data. They store and retrieve it.
Organizations dedicate file servers to store and share files within a network. Each server type has a role. It is to ensure smooth digital experiences and efficient data use. By knowing their distinct functions, businesses can better tailor their servers.
Introduction To Server Technology
An Introduction to Server Technology serves as the cornerstone of the digital world, powering everything from websites to applications. Understanding servers is essential for anyone delving into the realm of computing. Let’s embark on a journey to unravel the complexities of server technology and its pivotal role in modern computing.
The Role of Servers In Modern Computing
Servers are the powerhouse behind the seamless experience we encounter online. Their primary job is to store, process, and manage data for other computers or devices connected to a network. Imagine a busy restaurant kitchen; servers operate similarly, constantly preparing and delivering data orders to your screen.
- Web servers dish out website content.
- Email servers handle sending and receiving messages.
- Database servers organize and retrieve complex data.
Understanding Servers and Their Role in Modern Computing
The evolution of technology, from the first computers to modern-day networks, has transformed how we store and access data. A critical component of this evolution is the server—a device or program that provides services to other devices, known as clients.
But what is a server, and how do systems like web servers and server racks enable seamless connectivity in today’s digital world?
What Is a Server?
In simple terms, a server is a computer or system that provides data, resources, or services to other devices on a network. These devices, called clients, request services. These include hosting a website, running apps, or storing files.
For example, web servers are specialized systems designed to deliver websites to users’ browsers. When you type a URL into a browser, the web server processes the request and sends the necessary data back to display the webpage.
Servers can come in various forms, from standalone machines to highly specialized hardware installed in server racks. List servers.
What are server racks and their purposes?
Server racks are physical structures designed to house multiple servers securely. These racks provide organization, airflow, and easy access for maintenance. A server rack mount refers to the standardized dimensions and mounting equipment used to secure servers within a rack.
There are several types of server racking systems, including:
-
Rack-mount racks: These racks hold servers horizontally, making them ideal for data centers. Rack mount rack.
-
Open Frame Racks: lightweight and designed for areas with controlled environments.
-
Enclosed Racks: Provide additional security and better airflow management for servers.
Server racks use space well by organizing servers. They keep critical infrastructure accessible and running.
The Role of Servers in Modern Computing
Servers are essential. They power websites, apps, and cloud storage. Here’s a breakdown of different types:
-
Web Servers: handle HTTP requests, enabling users to access websites.
-
Application Servers: Run software applications for multiple users.
-
File Servers: Store and manage files for network users.
For businesses managing multiple servers, creating a list server helps organize and track tasks. Using tools to maintain a list server database ensures streamlined workflows in large-scale operations.
How Were Servers Used in the First Computers?
The concept of servers dates back to the first computers, which were massive machines used primarily for centralized tasks. Early servers operated within local networks, sharing resources among a limited number of clients. Today, server technology has advanced significantly, enabling global connectivity and cloud computing.
Modern servers use advanced hardware installed in server racks to handle massive workloads. They run in data centers worldwide. They support everything from streaming services to online transactions.
Choosing the Right Server Solution
Selecting a server depends on your needs. For businesses or tech projects, investing in reliable hosting and domain solutions is crucial. If you’re setting up a web server, start by exploring high-quality hosting plans or server racks for physical setups.
Explore Server Tools and Hosting Solutions
Looking to enhance your server infrastructure? Check out these exclusive deals:
Reference Sources
-
Introduction to Servers: Microsoft Documentation
-
Understanding Server Racks: TechTarget
-
History of Servers and Networking, Computer History Museum
Types of Servers: A Brief Preview
Dive into the diverse ecosystem of server types, each designed for specific tasks. From robust enterprise-level servers to compact home servers, the variety is vast.
| Server Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Web Server | Delivers web pages to users’ browsers |
| File Server | Stores and manages files for network users |
| Mail Server | Processes and stores emails |
| Application Server | Hosts and runs specific applications |
| Database Server | Provides database services to other machines |
| Virtual Server | Simulates a physical server environment |
Each server type plays a unique role in the digital ecosystem. Understanding these roles helps navigate the tech landscape with ease.

Credit: www.spiceworks.com
Web Servers: Gateways To The Internet
Imagine a door that opens up to countless books, pictures, and videos. Web servers are like these magical doors to the online world. They hold websites and let us see them on our computers and phones. Let’s dive into how they work and which ones are most popular.
Functionality And Primary Uses
Web servers have a big job. They send web pages to people’s browsers. This happens when someone types a web address or clicks a link. Web servers make sure the right page shows up.
- Host Websites: They keep all parts of a website.
- Deliver Content: They send the right content to users.
- Manage Traffic: They handle many people visiting a site at once.
- Improve Performance: They help websites load fast.
- Secure Data: They protect websites from malicious people.
Popular Web Server Software
Many web servers help websites work. Here are some that many people use:
| Name | Why People Like It |
|---|---|
| Apache | It’s free and very customizable. |
| Nginx | It’s adept at handling lots of visitors. |
| Microsoft IIS | It works well with Windows servers. |
| LiteSpeed | It’s quick and helps with security. |
Apache and Nginx are top choices for many websites. They both are powerful and can handle big websites. Microsoft IIS is a go-to for Windows users. LiteSpeed is newer, but it’s gaining fans for its speed and safety features.
Database Servers: Core Of Data Management
Database servers are powerful engines at the heart of data management. They store, organize, and retrieve data for applications and users. Imagine a digital library where data is the book and the database server is the librarian. This section explores the critical roles these servers play and the popular software that powers them.
Role In Data Storage And Retrieval
Database servers take the lead in storing information securely. They handle vast amounts of data with ease. When a user needs data, the server finds it quickly. This is vital for businesses that rely on quick data access.
- Secure storage: Protect data from unauthorized access.
- Efficient retrieval: Fetch data without delay.
- Concurrency control: Manage multiple data requests at once.
- Backup and recovery: Keep data safe and restore it if needed.
Examples Of Database Server Software
Many tools exist to manage data. Here are some leading database server software examples:
| Software | Type | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | Open-source | Web applications |
| Oracle Database | Commercial | Enterprise systems |
| Microsoft SQL Server | Commercial | Business intelligence |
| PostgreSQL | Open-source | Object-relational data |
| MongoDB | NoSQL | Big data and analytics |
Each software has unique features. They suit different business needs.
Application Servers: Facilitating Dynamic Content
Imagine a busy kitchen preparing different meals on demand. In the digital world, application servers are the chefs. They handle specific tasks to serve up dynamic content. These servers add power to websites, allowing users to interact with a page.
They make websites more than just static information. Let’s dive into how these servers work and why they matter.
How They Differ From Web Servers
Web servers and application servers are different. Web servers manage HTTP requests for static content. Think of them as librarians handing out books. Application servers go further. They can process complex operations. They create content on the fly, like chefs whipping up recipes. This makes websites interactive.
Here’s a simple comparison:
| Web Server | Application Server |
|---|---|
| Serves static content | Serves dynamic content |
| Handles HTTP requests | Handles various protocols |
| Simple file-based approach | Complex data-driven approach |
Use Cases And Popular Platforms
Application servers shine in different scenarios. They’re perfect for online banking, shopping carts, and forums. These platforms need to update often and quickly. They must respond to user inputs in real time.
Some well-known application servers include:
- Apache Tomcat: Often used for Java applications
- Microsoft IIS integrated with Windows servers
- WildFly: Known for its scalability
Each platform has its strengths. Apache Tomcat is excellent for Java environments. Microsoft IIS works well in Windows ecosystems. WildFly adapts easily to growing needs.
Here are common use cases:
- E-commerce sites: Manage user carts and payments
- Financial applications: Process transactions securely
- Social networks: update feeds and user interactions
File Servers: Centralized Data Storage Solutions
File servers play a crucial role in today’s digital world. They act as the beating heart of a network’s data storage. Imagine a treasure chest where all your digital gold is safe and sound. That’s what file servers do.
They keep all the files in one place for simple access. Let’s dive into why they are so important and the common ways they are set up.
Importance In Network Architecture
File servers are the backbone of network storage. They allow multiple users to share and manage files efficiently. Think of a busy office where everyone can open, edit, and save documents without a hitch. That’s file server magic at work. It ensures that all data is available when needed, without fuss.
Here’s a quick look at why they matter so much:
- Centralized security: one spot to protect rather than many.
- Easy backups: All files are copied from one place.
- Access control: Decide who sees what on the network.
- Streamlined management: One dashboard to rule all files.
Common File Server Configurations
Different setups suit different needs. Small offices may use a simple, standalone server. Big companies might need something more robust. Here are the usual types:
| Type | Description | Best for |
|---|---|---|
| Standalone | One server does it all. | Small teams. |
| Network-attached storage (NAS) | Connects to the network directly. | Easy setup and management. |
| Storage area network (SAN) | A network of storage devices. | Large businesses with significant data needs. |
| Cloud-based | Storage on the Internet. | Access files from anywhere. |
Each configuration has its perks. Standalone servers keep it simple. NAS offers a plug-and-play solution. SAN can handle a lot of data. Cloud-based servers let you work from anywhere. Choose the one that fits like a glove for your data needs.
Game Servers: Powering Multiplayer Gaming
Imagine playing a video game with friends around the world. Game servers make this possible. They are the powerhouses behind your favorite multiplayer experiences. Let’s dive into how these servers work and the challenges they face to keep gamers connected and engaged.
Working Principles Of Game Servers
At the heart of multiplayer gaming lies the game server. It’s a dedicated host that syncs player actions and game events. Think of it as a referee in a sports game, making sure everyone plays by the rules and knows the score.
- Connects players from different locations
- Processes in-game interactions and updates
- Ensures real-time communication for smooth play
A client-server model is often used. Players (clients) send data to the server. The server then processes this data, updates the game world, and sends it back to all clients.
Challenges In Managing Game Servers
Game servers must perform well to keep players happy. Speed and reliability are key. Yet, several challenges can arise:
| Challenge | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Lag | Delays in gameplay due to slow server response |
| Capacity | Server overload when too many players join |
| Security | Threats like DDoS attacks disrupting service |
| Updates | Implementing game patches without downtime |
Developers work hard to overcome these challenges. They optimize network code and server hardware. They also use load balancing and robust security measures to keep the gaming experience smooth and safe for everyone.
Proxy Servers: Mediators Between Users And The Web
Proxy servers act as intermediaries between users and the internet. They help in managing online traffic, improving security, and ensuring privacy. By serving as a gateway, proxy servers provide a valuable layer of abstraction and control.
Benefits Of Using A Proxy Server
- Improved Security: Proxy servers add an extra security layer between your computer and the internet.
- Faster Speeds: They can cache popular websites, which speeds up access.
- Access Restricted Content: Proxies can bypass geographic restrictions, allowing access to blocked content.
Security Features And Anonymity
Proxy servers enhance security through various features:
- Data Encryption: Encrypts data before it travels over the internet.
- IP Masking: Hides your real IP address, shielding your identity and location.
- Malware Scans: Scans incoming data for malware, protecting your system.
These features ensure users surf the web safely and anonymously.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Mail Servers: Handling Digital Communication
Mail servers are pivotal in managing digital communications. They process, send, and store emails. This ensures smooth communication in the digital world. Let’s delve deeper into how these servers operate and the security measures essential for their efficiency.
Process Of Sending And Receiving Emails
Emails move through a series of steps to reach their destination:
- User sends an email: This starts with composing and hitting send.
- Email server processing: The server receives and routes the message.
- Transfer to recipient’s server: The email moves to the recipient’s email server.
- Recipient receives the email: The final step is where the email appears in the recipient’s inbox.
This process is facilitated by SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) for sending and either POP (Post Office Protocol) or IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol) for receiving.
Security Measures For Mail Servers
Security is crucial for protecting both the server and the emails it handles.
- Encryption: Ensures that data is scrambled and unreadable to unauthorized parties.
- Spam filters: These block harmful or unwanted emails from reaching inboxes.
- Authentication: Verifies that users and servers are who they claim to be.
- Regular updates: Keeps the server software up-to-date against threats.
By implementing these security measures, mail servers can safeguard sensitive information and ensure reliable email delivery.
Choosing The Right Server For Your Needs
Choosing the right server for your business can feel like navigating a maze. With so many options, it’s crucial to find the perfect fit. This guide breaks down what to consider and how to balance performance with cost.
Factors To Consider
Determining the ideal server starts with understanding your needs. Consider these key points:
- Type of application: What software will run on the server?
- Traffic volume: How many users will access the server?
- Storage requirements: How much data will you store?
- Security: What level of protection do you need?
- Scalability: Will your server need to grow with your business?
Comparing Performance And Cost
Making a smart server choice involves weighing performance against expense.
| Server Type | Performance | Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Shared Server | Basic, shared resources | Low |
| Virtual Private Server (VPS) | Better, isolated resources | Medium |
| Dedicated Server | Top-notch, exclusive resources | High |
| Cloud Server | Scalable, pay-as-you-go | Variable |
Match server capabilities with your business demands to make the best choice.
Future Trends In Server Technology
Server technology is always evolving. New trends shape how we store and process data. These changes bring faster, smarter, and more efficient servers. Let’s explore what the future holds for server technology.
Emerging Technologies To Watch
Several key technologies are set to transform servers:
- Quantum Computing: This uses quantum bits to outperform traditional servers.
- Edge Computing: Data gets processed closer to its source, reducing latency.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI optimizes server operations and predicts maintenance needs.
- Energy-efficient Servers: Green technology reduces power consumption.
These technologies promise to revolutionize data centers worldwide.
The Impact Of Cloud Computing On Server Architecture
Cloud computing has greatly influenced server design. It offers scalable resources and services over the internet. With the cloud, server architecture has evolved:
| Traditional Servers | Cloud-Enabled Servers |
|---|---|
| Fixed resources | Scalable resources |
| On-premises | Remote access |
| Upfront cost | Pay-as-you-go |
| Regular maintenance | Managed services |
Cloud computing allows for flexible and efficient server management. It supports the shift to a more adaptable and cost-effective server infrastructure.

Credit: visual.ly
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Different Types Of Servers?
Different types of servers include web servers, file servers, database servers, application servers, mail servers, and virtual servers. Each type is designed for specific tasks and services within a network.
What Is The Basic Understanding Of Servers?
A server is a computer system that provides data, resources, or services to other computers, known as clients, over a network. Its primary function is to manage network resources and support data exchange.
What Are The Different Types Of File Servers?
Different types of file servers include dedicated file servers, nondedicated file servers, and virtual file servers. Each serves distinct file management roles within a network.
What Is Server Classification?
Server classification involves categorizing servers based on their purpose, performance, and size. This helps in identifying the right server type for specific tasks or business needs.
Conclusion
Navigating the landscape of server types can be daunting. From robust dedicated servers to flexible cloud options, each has its merits. Your choice hinges on specific business needs and budget constraints. As you weigh your options, remember that the right server fuels efficiency and growth.
Looking to enhance your server infrastructure? Check out these exclusive deals:
- Affordable Hosting Plans for Web Servers
- Domain Registration Deals for Your Projects
- Software Discounts for Managing Server Tasks
Choose wisely, and your digital infrastructure will become a powerful asset for success.